[Reference /引用はこちら]
Chengshuo Xia, and Yuta Sugiura, Wearable Accelerometer Layout Optimization for Activity Recognition Based on Swarm Intelligence and User Preference, in IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 166906-166919, 2021. [DOI]
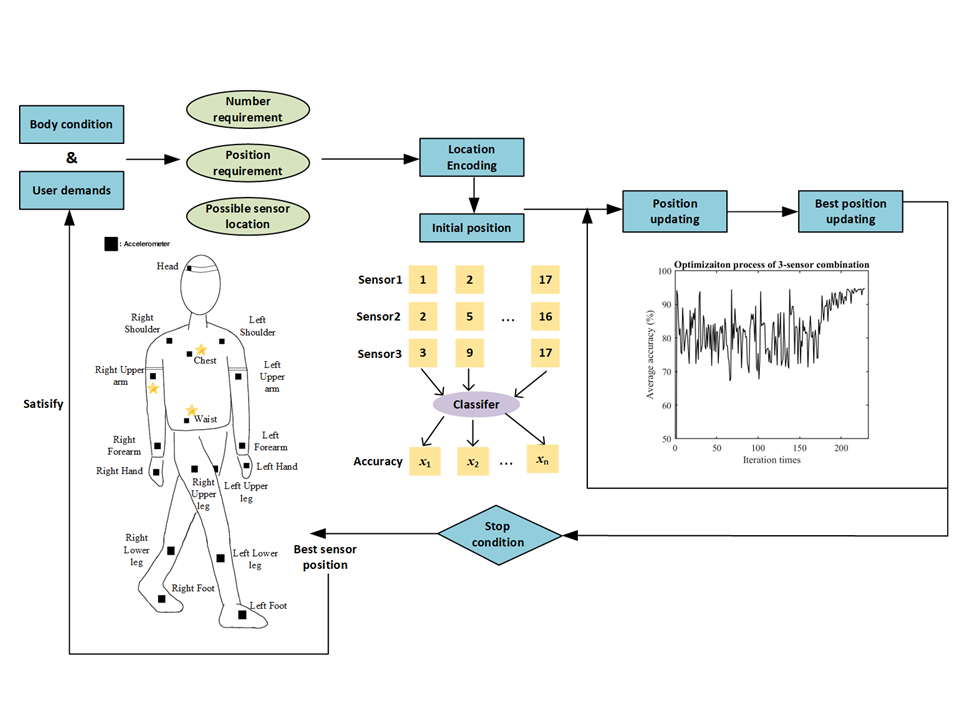
人間の行動を認識する Human activity recognition(HAR)システムは、ヒューマン・コンピュータ・インタラクション、ユビキタス・コンピューティング、機械学習の分野の中で非常に注目されている研究分野である。機械学習と組み合わせた従来の HAR システムのインタフェースは、ユーザに対するセンサ位置が固定されている。センサ位置が変動すれば、認識精度が変化し新たな学習データセットが必要となる。従って、最適なセンサ位置を得ることは HAR システムの設計において重要な役割を果たす。そこで本論文では、より少ない計算コストで最適なセンサの位置や組み合わせを見つけ出すための新しい最適化手法を提案する。具体的には、多段階かつ多群の離散粒子群最適化(MSMS-DPSO)アルゴリズムを開発し、センサ数に対応した最適なセンサの組み合わせと認識精度の傾向を探索する。さらに、ユーザごとのセンサ位置の嗜好に応じて、ユーザの要求や身体的条件に基づいた適切なセンサのレイアウトを設計することも可能である。設計手法の検証のために主に 3 つの実験を行った。実験の前準備として 10 名のユーザに Xsens スーツを着用させ 10 種類の動作を行わせることで、IMU(慣性計測装置)のデータセットを形成した。1 つ目の実験では、3 種類のサンプリングレートのデータセットを用いて、認識精度に対応するセンサ数の推移に対するサンプリングレートの影響を探った。その後提案する MSMS-DPSO アルゴリズムを用いて、異なるセンサ数の条件下で最適なセンサの組み合わせを導出する.ベースライン法としては、全てのセンサの組み合わせを走査する動的計画法を選択した。2 つ目の実験では、提案する最適化スキームの有効性を検証するために、5 種類の分類器をテストした。3つ目の実験では、センサの装着に関するユーザの嗜好を収集するためにオンライン調査を行った。提案手法を用いることで、異なるユーザの嗜好に適合させつつ、最高の認識精度と少ない計算時間で最適なセンサ位置や組み合わせを求めることが可能であることを確認した。本論文で提案した手法は、ウェアラブル HAR システムにとって最適なセンサ位置と組み合わせを見つけ出し、異なる個人の状況に応じてより柔軟な HAR システムの設計の支援を実現する。
Wearable intelligent systems that recognize the daily activities of humans have significantly contributed to many useful applications. However, in practical wearable applications, the target individuals may have different body conditions and demands in terms of sensor wearing. Sensors may return different information depending on their placement, which to some extent determines the quality of a recognition system. Obtaining the optimal sensor positions with the highest recognition accuracy plays a significant role in activity recognition design. To contribute to a flexible and user-friendly wearable sensor layout, this paper designed a multistage and multiswarm discrete particle swarm optimization algorithm to explore the best sensor combinations and accuracy trends corresponding to different requirements of sensor numbers. The proposed optimization scheme is applied to investigate the influences that different numbers and placements of wearable accelerometers have on an activity recognition system. Furthermore, to address the issue of user preference regarding the sensor position, a relevant sensor layout can also be designed based on the demands and physical condition of the subject. The proposed method can determine the best sensor position (combinations) with lower computational cost for various activity recognition systems.