画像解析による頚椎可動域角度計測補助システム
Cervical Spine Range of Motion Measurement Utilizing Image Analysis
2021
藤田浩二*,松尾佳奈*,小山恭史,歌川蔵人,森下真伍,杉浦裕太(*共同筆頭著者)
Koji Fujita*, Kana Matsuo*, Takafumi Koyama, Kurando Utagawa, Shingo Morishita, Yuta Sugiura (*These authors contributed equally to this work)
[Reference /引用はこちら]
Koji Fujita*, Kana Matsuo*, Takafumi Koyama, Kurando Utagawa, Shingo Morishita, Yuta Sugiura (*These authors contributed equally to this work), Development and testing of a new application for measuring motion at the cervical spine, BMC Medical Imaging, Vol.22, Article number 193. 2022-11-22. [DOI]
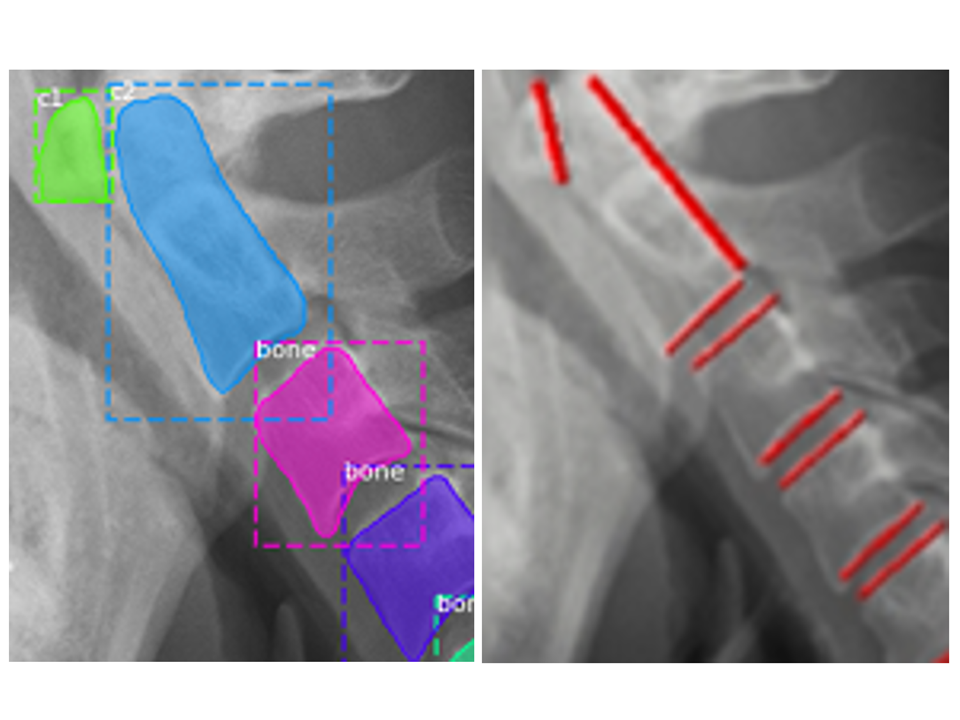
頚椎の疾患は他の部位の疾患に比べしばしば重大な日常生活動作の障害をもたらすため,迅速かつ正確な診断が要求される.頚椎の疾患を診断する指標の1つとして可動域角度を測ることがある.主な計測手法は手動であり医師にとって負担となっている.本研究では,Mask R-CNN と画像処理を用いて頚椎レントゲン画像から頚椎の可動域角度を計測できないか検討する.提案する頚椎可動域角度計測システムにおいて可動域角度を計測した結果,真値との平均誤差が3.5度,標準偏差が2.8 度であった.また提案システムと頚椎の診断を専門としない研修医の精度を比べた結果,計測精度は同程度であることがわかった.提案システムは研修医と同等の精度かつ計測値のばらつきなく頚椎可動域角度を計測できた.
BackgroundCervical myelopathy is a progressive disease, and early detection and treatment contribute to prognosis. Evaluation of cervical intervertebral instability by simple X-ray is used in clinical setting and the information about instability is important to understand the cause of myelopathy, but evaluation of the intervertebral instability by X-ray is complicated. To reduce the burden of clinicians, a system that automatically measures the range of motion was developed by comparing the flexed and extended positions in the lateral view of a simple X-ray of the cervical spine. The accuracy of the system was verified by comparison with spine surgeons and residents to determine whether the system could withstand actual use.
Methods
An algorithm was created to recognize the four corners of the vertebral bodies in a lateral cervical spine X-ray image, and a system was constructed to automatically measure the range of motion between each vertebra by comparing X-ray images of the cervical spine in extension and flexion. Two experienced spine surgeons and two residents performed the study on the remaining 23 cases. Cervical spine range of motion was measured manually on X-ray images and compared with automatic measurement by this system.
Results
Of a total of 322 cervical vertebrae in 46 images, 313 (97%) were successfully estimated by our learning model. The mean intersection over union value for all the 46-test data was 0.85. The results of measuring the CRoM angle with the proposed cervical spine motion angle measurement system showed that the mean error from the true value was 3.5° and the standard deviation was 2.8°. The average standard deviations for each measurement by specialist and residents are 2.9° and 3.2°.
Conclusions
A system for measuring cervical spine range of motion on X-ray images was constructed and showed accuracy comparable to that of spine surgeons. This system will be effective in reducing the burden on and saving time of orthopedic surgeons by avoiding manually measuring X-ray images.
Trial registration Retrospectively registered with opt-out agreement.