User Authentication Method for Hearables Using Sound Leakage Signals
2023
雨坂宇宙,渡邉拓貴,杉本雅則,杉浦裕太,志築文太郎
Takashi Amesaka, Hiroki Watanabe, Masanori Sugimoto, Yuta Sugirua, Buntarou Shizuki
[Reference /引用はこちら]
Takashi Amesaka, Hiroki Watanabe, Masanori Sugimoto, Yuta Sugirua, and Buntarou Shizuki, EarLock: Personal Authentication System for Hearables Using Sound Leakage Signals, in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing. [DOI]
Takashi Amesaka, Hiroki Watanabe, Masanori Sugimoto, Yuta Sugirua, and Buntarou Shizuki. User Authentication Method for Hearables Using Sound Leakage Signals, In Proceedings of ISWC 2023, Cancun, Quintana Roo, Mexico, 2023. [DOI]
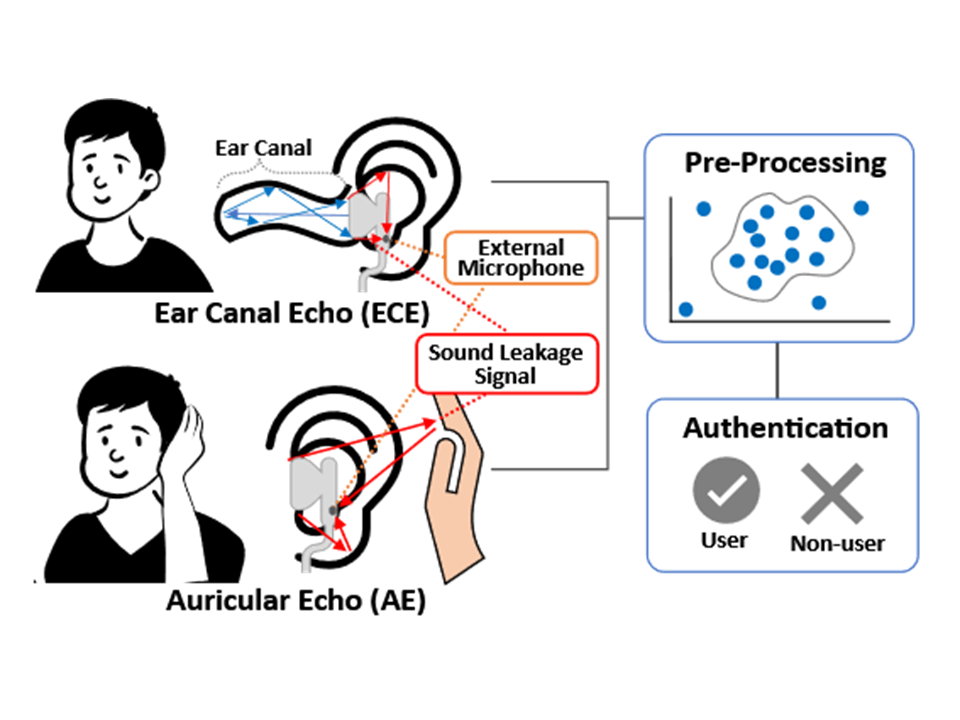
本論文では,ヒアラブルデバイスからの音漏れ信号を利用した新しい生体認証手法を提案する.音漏れ信号は,外耳道,耳介,手の音響特性を示し,ユーザによって異なる.提案手法は,スピーカーと外部マイクによる実装が可能であるためヒアラブルデバイスへの適応性が高い.また,耳介の生体特性を新たに取得しているため,既存手法と組み合わせて利用できる可能性がある.本研究では,物理モデルを用いて音漏れ信号の特性を調べ,プロトタイプデバイスを用いてデータを測定し提案手法の認証性能を調査した.
Earphone-type wearable devices, also known as “hearables,” will have many functions in the future. Some of those functions will require authentication of the wearer for access to the user’s privacy information or settlement of payments. In this study, we propose a new personal authentication system for hearables called EarLock. EarLock authenticates the wearer by acquiring and analyzing ear canal and auricle shape information using sound leakage from the device. The system can be implemented using a speaker and external microphone that are highly compatible with hearables. We implemented three prototype devices and investigated EarLock’s authentication performance under various practical scenarios, including walking conditions, noisy environments, and situations with object interference. Experimental results showed that the in-ear, open-ear, and bone-conduction devices achieved balanced accuracy (BAC) scores of 87.2–93.7%, 83.4–94.7%, and 85.9–90.0%.